How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding fundamental components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and adhering to crucial safety regulations. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable flight experience every time.
We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, explaining their functions and common troubleshooting techniques. We’ll then move on to pre-flight procedures, basic flight controls, GPS navigation, camera operation, and legal considerations. Finally, we’ll touch upon advanced techniques and maintenance practices to help you prolong the life of your drone.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the key parts of a typical drone, explain their roles, and provide a glossary of common terms.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone consists of several interconnected components working together to achieve flight. Let’s examine the major parts and their functionalities.
| Component | Function | Common Issues | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust for lift and control. | Bent or damaged propellers, imbalance. | Inspect for damage; replace if necessary; balance propellers. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, providing power. | Motor failure, overheating. | Check motor connections; allow for adequate cooling. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, controlling all aspects of flight. | Software glitches, sensor errors. | Check firmware updates; recalibrate sensors. |
| Battery | Powers the drone’s motors and electronics. | Low battery, damaged cells. | Monitor battery levels; replace when necessary. |
| GPS | Provides location data for navigation and stability. | Weak signal, interference. | Fly in open areas with a clear view of the sky. |
| Camera | Captures photos and videos. | Poor image quality, malfunctioning lens. | Adjust camera settings; check for obstructions. |
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms will enhance your understanding and operation.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a consistent altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, reducing vibrations.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A function that automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point.
- Waypoint Navigation: A feature that allows the drone to fly to pre-programmed points.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of the motors.
- Firmware: The software that controls the drone’s functions.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures

Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is essential to ensure safe and successful operation. This involves checking the drone’s components, assessing environmental conditions, and understanding potential hazards.
Pre-Flight Checklist
This checklist should be followed meticulously before every flight.
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Check battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify GPS signal strength (at least 8 satellites).
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check for any visible damage to the drone.
- Review local regulations and airspace restrictions.
- Assess wind conditions and weather forecast.
Pre-Flight Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight process helps ensure all steps are completed.
(Illustrative description: The flowchart would begin with “Power On Drone,” branching to “Check Battery Level” and “Check Propellers.” If either check fails, it would lead to “Troubleshooting.” If both pass, it moves to “Check GPS Signal,” then “Calibrate Compass,” then finally “Ready for Takeoff.”)
Best Practices for Safe Drone Operation Before Takeoff
These practices enhance flight safety.
- Always visually inspect the drone before each flight.
- Never fly near airports or restricted airspace.
- Be mindful of obstacles and potential hazards.
- Always keep the drone within visual line of sight.
- Never fly in adverse weather conditions.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the basic flight controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section covers the control sticks, takeoff, hovering, landing, and various flight modes.
Drone Control Sticks
Most drones use two control sticks: one for controlling altitude and movement, the other for directional control.
- Left Stick (Throttle/Pitch): Controls altitude (up/down) and forward/backward movement.
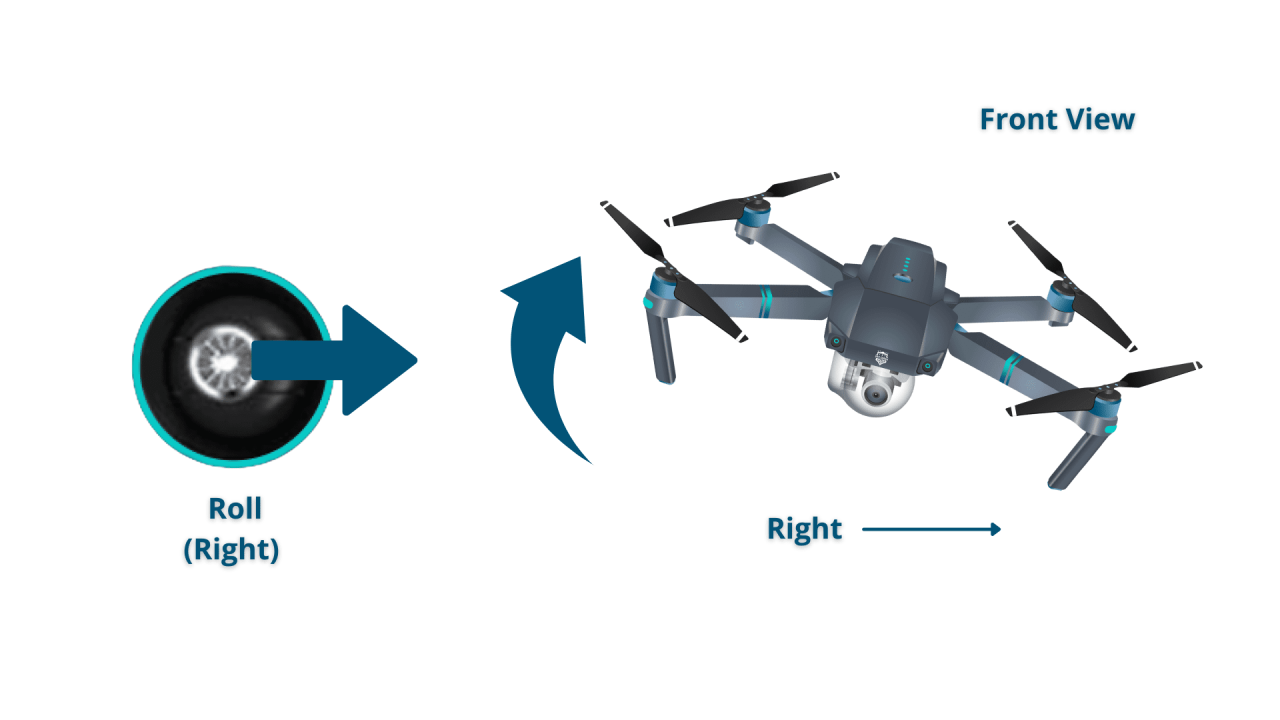
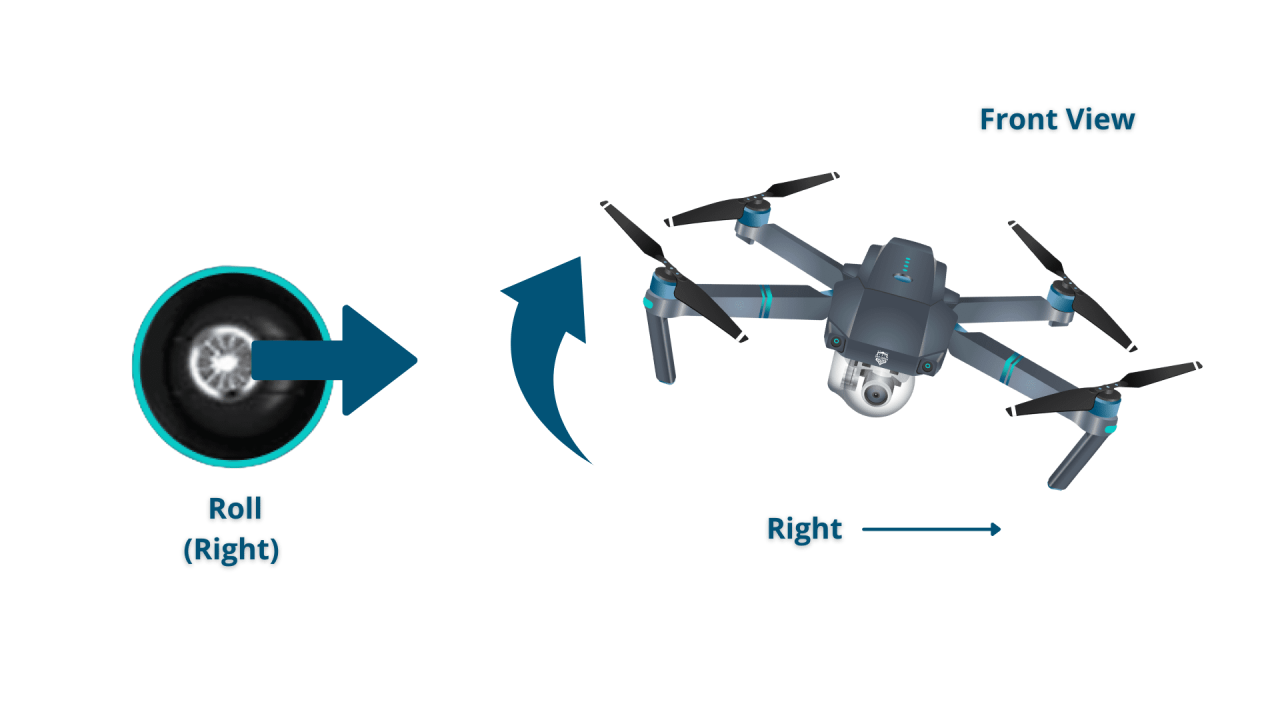
- Right Stick (Roll/Yaw): Controls left/right movement (roll) and rotation (yaw).
Takeoff, Hovering, and Landing Procedures
These procedures are essential for safe drone operation.
- Takeoff: Gently raise the left stick to initiate ascent. Maintain a steady hover.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air using small adjustments to the control sticks.
- Landing: Slowly lower the left stick to descend and land gently.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to varying skill levels and flight scenarios.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Increases speed and responsiveness, for experienced pilots.
- Manual Mode: Offers full control over the drone, requiring significant skill.
Navigating and Using GPS Features: How To Operate A Drone
GPS plays a vital role in drone navigation, stability, and safety features. This section details how to utilize GPS functionality for enhanced flight control and autonomous operations.
The Role of GPS in Drone Navigation and Stability
GPS provides the drone with its location, allowing for precise navigation and stability. It enables features like Return-to-Home and waypoint navigation.
Using GPS Features: RTH and Waypoint Navigation
These GPS-enabled features enhance drone control and flight planning.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically guides the drone back to its takeoff point, useful in case of signal loss or low battery.
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows pre-programming a flight path, enabling autonomous flight to specific locations.
Potential GPS Interference Sources

Several factors can affect GPS signal strength and accuracy.
- Tall buildings and structures: Obstruct GPS signals.
- Dense foliage: Can weaken signal strength.
- Weather conditions: Heavy rain or snow can interfere with GPS reception.
- Electromagnetic interference: From other electronic devices.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and modes. This section provides guidance on optimizing camera settings and capturing stunning footage.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Camera settings directly impact image quality. Adjusting these parameters allows for creative control.
- Resolution: Higher resolution means larger file sizes but better image detail.
- Shutter Speed: Controls motion blur; faster speeds freeze motion, slower speeds create motion blur.
- ISO: Controls sensitivity to light; higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can increase noise.
Camera Modes
Different camera modes provide various creative options.
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records video footage.
- Timelapse Mode: Captures a series of photos at set intervals, which can be combined into a timelapse video.
Tips for Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
These tips ensure you get the best possible results.
- Use a gimbal for smooth, stable footage.
- Shoot in good lighting conditions.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Consider the composition of your shots.
- Use editing software to enhance your footage.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation requires adherence to safety guidelines and relevant regulations. This section highlights essential safety precautions and legal considerations.
Guidelines for Safe Drone Operation
These guidelines ensure safe and responsible drone operation in various environments.
- Urban Areas: Maintain a safe distance from people and buildings.
- Near Airports: Check for airspace restrictions and never fly near airports without proper authorization.
- Open Areas: Be aware of potential hazards like power lines and wildlife.
Drone Regulations and Legal Requirements
Familiarize yourself with local laws and regulations concerning drone operation.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires knowledge of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all these elements, including practical tips and troubleshooting advice, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, proficient drone piloting comes with practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and its limitations.
(Note: Specific regulations vary significantly by region. This section should be supplemented with information relevant to the user’s location.)
Safety Precautions
These precautions help prevent accidents.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone.
- Never fly in adverse weather conditions.
- Be aware of surrounding airspace and avoid restricted areas.
- Follow all manufacturer instructions and guidelines.
- Keep your drone’s firmware updated.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section addresses common drone problems, offering solutions and preventative measures.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, battery damage | Charge the battery fully; replace if damaged | Monitor battery levels; use high-quality batteries |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, interference | Fly in open areas; restart the drone | Avoid flying near tall buildings or in dense foliage |
| Motor Failure | Motor damage, loose connections | Inspect motors; check connections; replace if necessary | Regularly inspect the drone for damage |
| Unstable Flight | Calibration issues, sensor problems | Calibrate the sensors; update firmware | Regularly calibrate sensors |
Advanced Drone Techniques
For experienced users, advanced techniques can significantly enhance flight capabilities and data acquisition. This section explores some of these advanced maneuvers and operational strategies.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
These maneuvers require significant skill and practice. (Note: Specific maneuvers depend heavily on the drone model. Examples might include flips, rolls, and other acrobatic movements.)
(Illustrative Description: A flip involves rapidly rotating the drone 360 degrees around a specific axis. This requires precise control stick manipulation and understanding of the drone’s response characteristics. Rolls involve rotating the drone along its longitudinal axis. These maneuvers should only be attempted in safe, open spaces with ample room for error.)
Drone Software for Flight Planning and Data Analysis
Specialized software enhances flight planning and post-processing.
(Illustrative Description: Software like Litchi allows users to plan complex flight paths with waypoints, altitudes, and other parameters. After the flight, the data can be analyzed to extract information such as flight time, distance covered, and other relevant metrics.)
Calibrating Drone Sensors and Compass
Proper calibration ensures accurate flight and navigation.
(Illustrative Description: Calibration involves a series of steps where the drone is held stationary while its sensors are initialized. This process ensures that the drone accurately measures its orientation and position. The compass calibration usually involves rotating the drone 360 degrees to align it with the Earth’s magnetic field.)
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Proper maintenance and storage significantly extend the lifespan of your drone and its components. This section Artikels a regular maintenance schedule and proper storage techniques.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Regular cleaning and inspection are crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
- Weekly Inspection: Check for loose screws, damaged propellers, and general wear and tear.
- Monthly Cleaning: Gently clean the drone body and propellers with a soft cloth.
- Quarterly Inspection: Thoroughly inspect all components, including motors, battery, and flight controller.
Tips for Proper Storage
Proper storage prevents damage and extends the drone’s lifespan.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Keep the battery charged to around 50% to avoid overcharging or deep discharge.
- Store the drone and its accessories in a protective case to prevent damage during transportation.
Correct Drone Storage, How to operate a drone
(Illustrative Description: The drone should be stored in a protective case, preferably with its propellers removed and stored separately. The battery should be stored separately, ideally in a dedicated battery case. All accessories, such as charging cables, remote controllers, and extra propellers, should be neatly organized within the case. The case should be kept in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture.)
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has provided a solid foundation, covering everything from basic flight controls to advanced techniques and safety regulations. By understanding your drone’s components, adhering to pre-flight checklists, and practicing responsible flight, you can unlock the potential of aerial photography and videography while ensuring the safety of yourself and others.
Remember to always prioritize safety and stay informed about local regulations. Happy flying!
Key Questions Answered
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which provides comprehensive guidance. From there, practice and familiarity will build your confidence and skills in operating a drone safely and effectively.
For beginners, a ready-to-fly drone with GPS and assisted flight modes is recommended. These features simplify control and enhance stability.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for an estimated flight time; expect shorter flight times in colder weather or with heavier payloads.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Losing GPS signal can cause instability. Most drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function, but maintaining visual contact and carefully bringing the drone down manually is crucial.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is recommended before each flight session, especially if you’ve transported your drone or experienced significant magnetic interference.